The main concern of our research theme Antiparasitic agents supervised by Joëlle Dubois is to find new antiparasitic agents to fight against protozoan parasites responsible for tropical diseases (malaria, African sleeping sickness, Chagas disease, …). Three axes have been developped: protein farnesyltransferase inhibition, total synthesis of antiparasitic natural products and fluorescent probe design and synthesis for biological studies.
Protein farnesyltransferase inhibitors
Protein farnesyltransferase (FTase) is a zinc metalloenzyme that catalyzes the addition of the isoprenoid farnesyl to a cysteine residue located in the C-terminal part of certain cell signaling proteins. This post-translational modification is essential for the functioning of these proteins. Protein farnesyltransferase (FTase), initially studied for anticancer therapy, was further validated as an antiparasitic target. The main purpose of our work is to obtain new FTIs with potent antiparasitic activities.
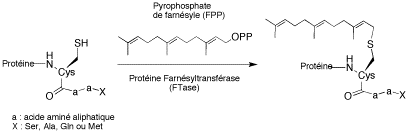
The search for new FTIs was realized according two approaches:
- rational design of inhibitors around the imidazole ring.
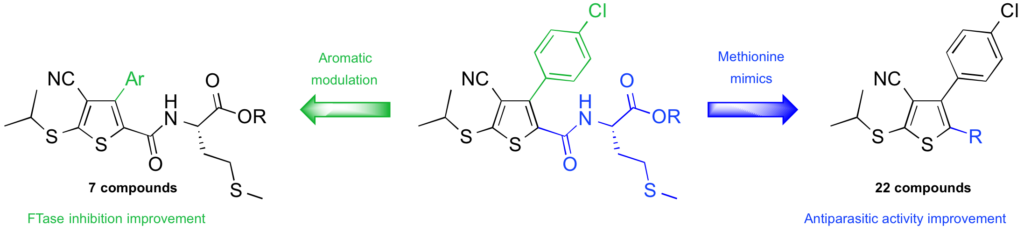
- screening of ICSN chemical library lead to the discovery a new FTI family with a 3-arylthiophene scaffold. Structure-Activity Relationship studies were realized.
Arylthiophenes
D. Bosc, E. Mouray, S. Cojean, C.H. Franco, P.M. Loiseau, L.H. Freitas-Junior, C.B. Moraes, P. Grellier, and J. Dubois ; Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 173-186.
Highly improved antiparasitic activity after introduction of an N-benzylimidazole moiety on protein farnesyltransferase.
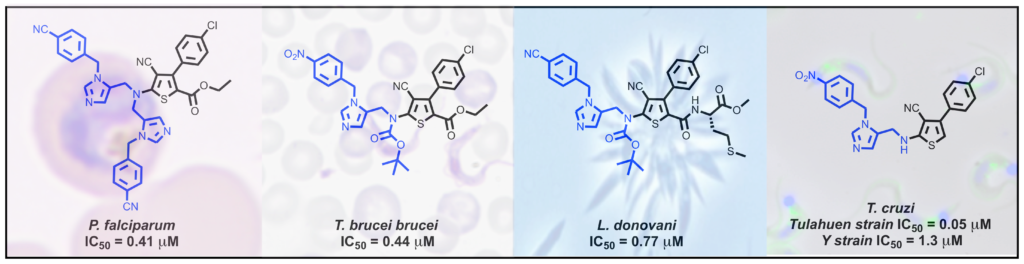
Twenty four new derivatives were synthesized and evaluated against human and parasite farnesyltransferases, and their anti-parasitic activity was determined against P. falciparum, T. brucei, T. cruzi, and L. donovani. Introduction of a N-p-substituted-benzylimidazole led to significantly increase the inhibition of parasite proliferation in the submicromolar range. The structure of the best inhibitors was parasite dependent. Three compounds possess IC50 values at the same range as the reference miltefosine against L. donovani proliferation and other new derivatives display high level of anti-trypanosomal activity against T. cruzi, higher or in the same order of magnitude as the reference compounds benznidazole and nifurtimox.
DOI : 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.12.045
D. Bosc, E. Mouray, P. Grellier, S. Cojean, P.M. Loiseau and J. Dubois ; MedChemComm. 2013, 4, 1034-1041.
Introduction of methionine mimics on 3-arylthiophene : Influence on protein farnesyltransferase inhibition and on antiparasitic activity.
To investigate the influence of methionine residue on FTase and antiparasitic activities, 29 novel tetrasubstituted thiophenes bearing methionine or analogous moieties were synthesised. These new derivatives were evaluated on human and T. brucei protein farnesyltransferases and on proliferation of 4 protozoan parasites : P. falciparum, T. brucei, T. cruzi, and L. donovani. Low micromolar or submicromolar activities on T. b. brucei and L. donovani were obtained confirming the potential of this new class as antiparasitic agents.
DOI : 10.1039/c3md00065f
S. Lethu, D. Bosc, E. Mouray, P. Grellier and J. Dubois ; J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2013, 28, 163-171.
New protein farnesyltransferase inhibitors in the 3-arylthiophene series : diversification of the aryl moiety by solid phase synthesis.
A new synthetic pathway was devised to reach tetrasubstituted 3-arylthiophene 2-carboxylic acids in three-step solid phase synthesis. This very efficient methodology afforded 20 new compounds.
DOI : 10.3109/14756366.2011.643302

D. Bosc, S. Lethu, E. Mouray, P. Grellier and J. Dubois ; MedChemComm. 2012, 3, 1512-1517.
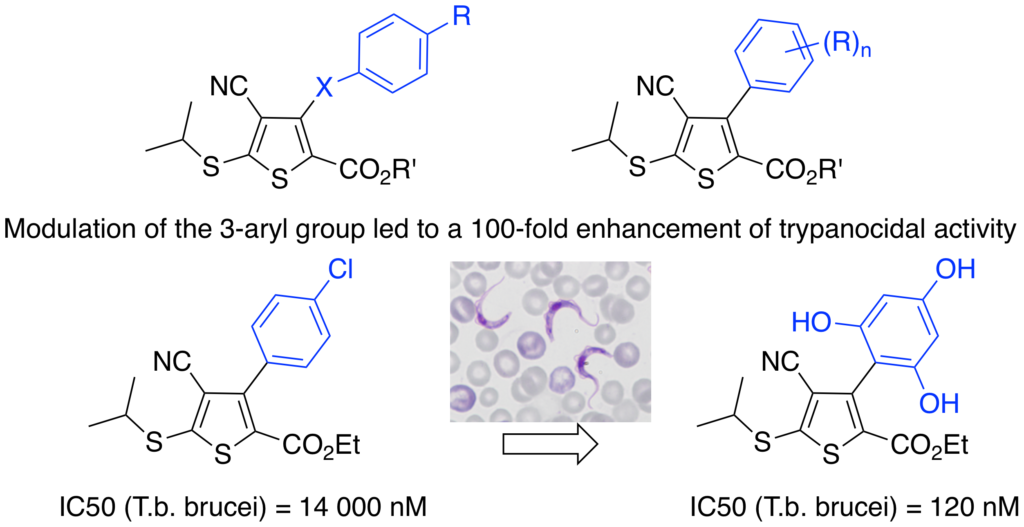
Improvement of the trypanocidal activity of 3-arylthiophene farnesyltransferase inhibitors by modulation of their 3-aryl group.
To improve solubility and cell penetration, modifications on the 3-aryl moiety were realized such as the introduction of heteroatoms or homologation of the aryl bond. Introduction of two or three hydroxyl groups really improved human and T. brucei FTase inhibition. The effect was more impressive on T. b. brucei proliferation by increasing the hit compound activity by two orders of magnitude, resulting in good submicromolar inhibitory activities.
DOI : 10.1039/C2MD20197F
S. Lethu and J. Dubois ; Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, (20-21), 3920-3931.
SNAr and palladium-catalyzed Reactions of deactivated thiophene : application to the synthesis of protein farnesyltransferase inhibitors.
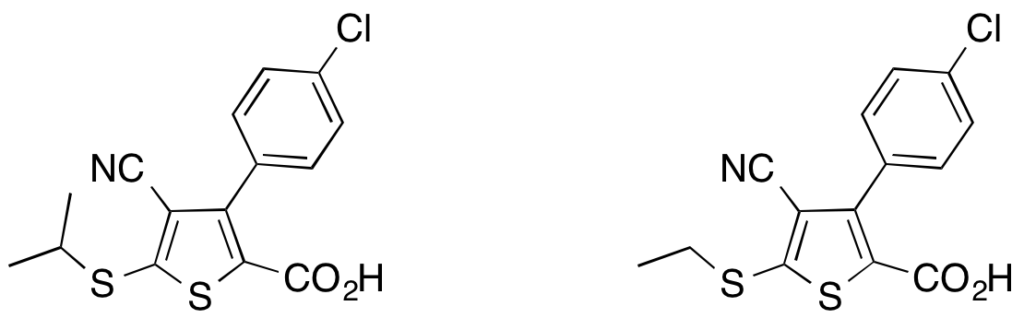
To investigate the influence of the 5-thioether moiety upon protein farnesyltransferase inhibition, a new library of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-cyanothiophene-2-carboxylic derivatives was synthesized through the application of aromatic nucleophilic substitutions benefiting from a sulfone-based leaving group and by direct palladium-catalyzed reactions on a thioalkylthiophene. This small library of ester derivatives and their corresponding acids was then evaluated for protein farnesyltransferase inhibitory activity ; some library members exhibited promising submicromolar activities.
DOI : 10.1002/ejoc.201100215
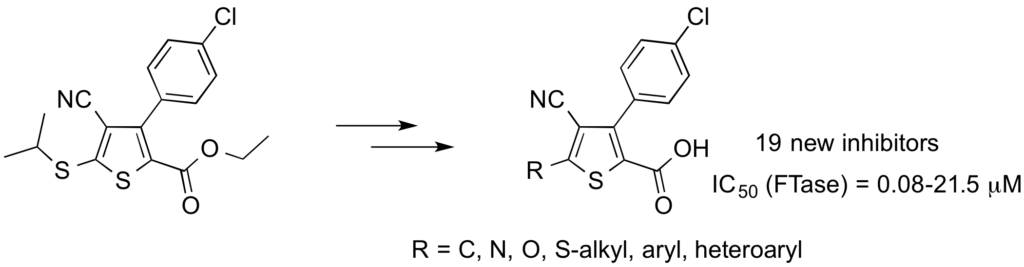
S. Lethu, M. Ginisty, D. Bosc and J. Dubois ; J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6205-6208.
Discovery of a New Class of Protein Farnesyltransferase Inhibitors in the Arylthiophene Series.
Screening of the ICSN chemical library led to the discovery of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-cyano-5-thioalkylthiophene 2-carboxylic acids as potent farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Enzymatic kinetic studies showed that this original FTI series belongs to the CaaX competitive inhibitor class. Preliminary SAR studies allowed us to improve the IC50.
DOI : 10.1021/jm901280q
Imidazoles
S. Duez, L. Coudray, E. Mouray, P. Grellier and J. Dubois ; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 543-556.
Towards the synthesis of bisubstrate inhibitors of protein farnesyltransferase : synthesis and biological evaluation of new farnesylpyrophosphate analogue.
With the aim of creating new bisubstrate inhibitors of FTase, new farnesyl pyrophosphate analogues have been studied. Farnesyl analogues with a malonic acid function exhibited the best inhibitory activity on FTase. This group was introduced into our imidazole-containing model leading to new compounds with submicromolar activities.
DOI : 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.12.017
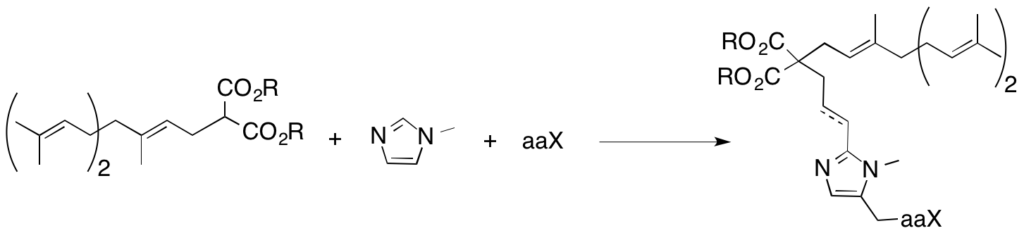
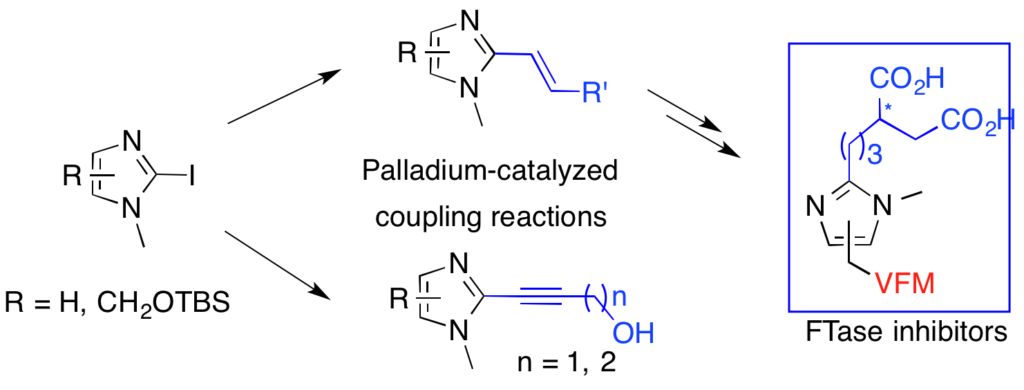
J. Kerhervé, C. Botuha and J. Dubois ; Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2214-2222.
New asymmetric synthesis of protein farnesyltransferase inhibitors via palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of 2-iodo-imidazoles.
Palladium catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of 2-iodoimidazole have been studied to synthesize imidazole-containing protein farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Suzuki coupling reaction proved to be very efficient to introduce functionalized alkyl chains at the 2-position of the imidazole ring and a new synthesis of the required alkenylboronates was realised by a reaction of cross metathesis. Asymmetric synthesis of allyl succinic derivatives allowed us to synthesize chiral protein farnesyltransferase inhibitors through Suzuki coupling and to determine the influence of the stereochemistry of our inhibitors on the enzymatic activity.
DOI : 10.1039/b902601k
L. Coudray, R.M. de Figueiredo, S. Duez, S. Cortial and J. Dubois ; J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 972-985.
Synthesis of imidazole containing analogues of farnesyl pyrophosphate and evaluation of their biological activity on protein farnesyltransferase.
Based on the transition state of the protein farnesyltransferase, a novel series of potential bisubstrate inhibitors has been designed and synthesized. The original structures are built around three elements, a prenyl moiety, a 1,4-diacid motif and an imidazole ring. All the compounds were evaluated for their ability to inhibit FTase and in vitro P. falciparum growth.
DOI : 10.1080/14756360802561196
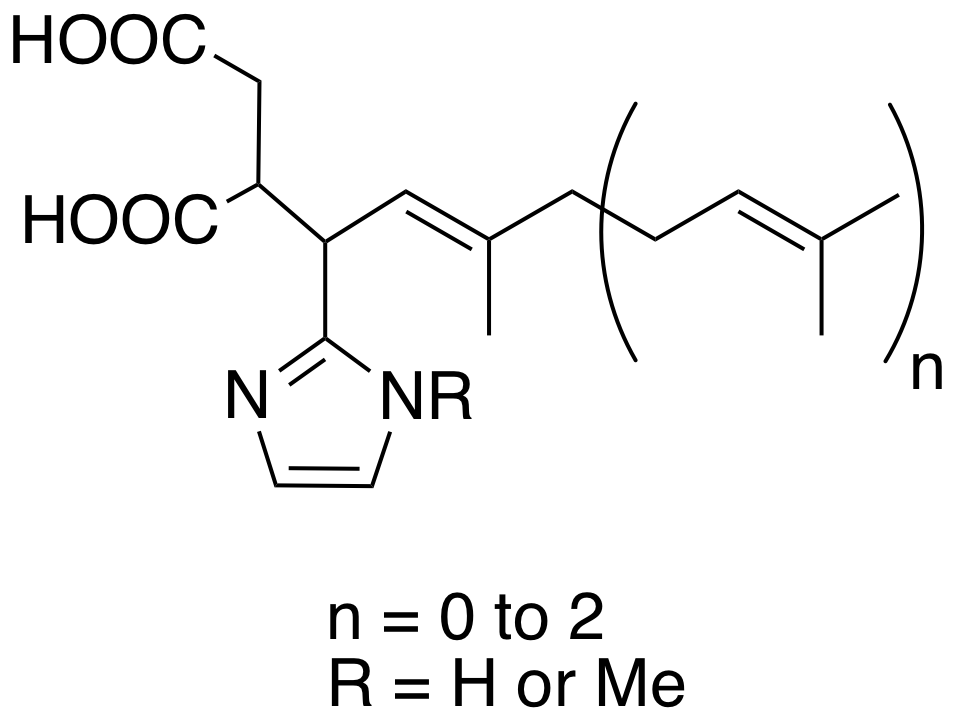
R.M. de Figueiredo, L. Coudray and J. Dubois ; Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 3299-3309.
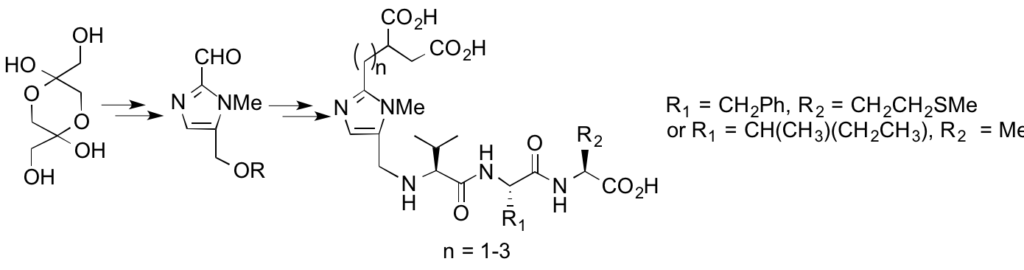
Synthesis and biological evaluation of potential bisubstrate inhibtors of protein farnesyltransferase. Design and synthesis of functionalized imidazoles.
A novel series of compounds, derived from 2,5-functionalized imidazole has been synthesized as potential bisubstrate inhibitors of protein farnesyltransferase using structure-based design. These compounds have a 1,4-diacid chain and a tripeptide connected by an imidazole ring. The synthetic strategy relies on the functionalization at the C-2 position of the heterocycle with the diacid side chain and peptide coupling at the C-5 position.
DOI : 10.1039/b709854e
Synthesis of antiparasitic natural products
Thévenin, M. ; Thoret, S. ; Dubois, J. ; Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 42, 5843-5852.
First total synthesis of original chalcone-flavone dimer as cissampeloflavone analogues.
The first example of a furoflavone synthesis closely related to the antiparasitic natural product, cissampeloflavone, was achieved through the flavone as key intermediate. Direct introduction of the acyl group during furan formation proved to be more efficient. Conjugate addition of an iodo- flavone to an ynone followed by intramolecular Heck cyclization gave the best results, leading to the first synthetic chalcone– flavone dimer ever described.
DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201800338
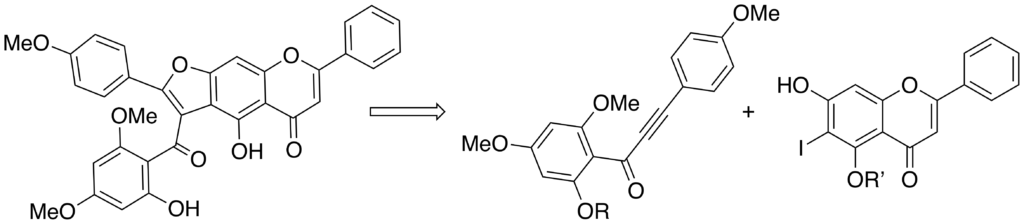
Grayfer, T. D. ; Grellier, P. ; Mouray, E. ; Dodd, R. H. ; Dubois, J. ; Cariou, K. ; Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 708–711.
Mallotojaponins B and C : Total Synthesis, Antiparasitic Evaluation, and Preliminary SAR Studies.
The first total syntheses of mallotojaponin B and C as well as several analogues have been achieved. Biological evaluation of the synthesized compounds against P. falciparum and T. brucei have also been carried out.
DOI : 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03676
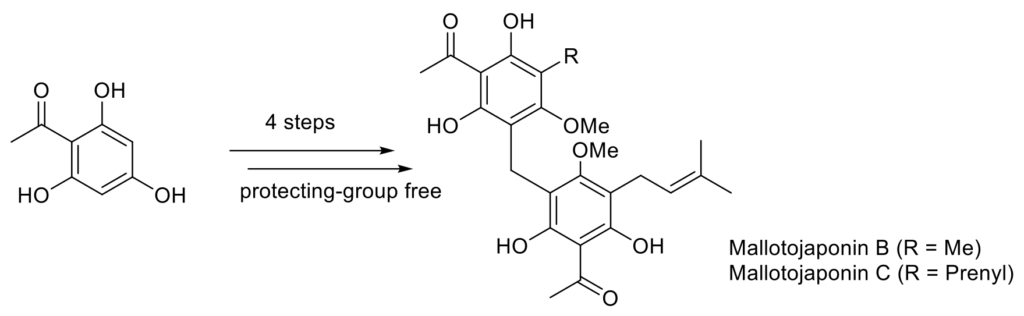
M. Thévenin, E. Mouray, P. Grellier and J. Dubois ; Eur. J. Org. Chem.2014, 2986-2992.
Facile formation of methylene bischalcones through unprecedented methylenation reaction. Application to antiparasitic agents and natural product synthesis.
The formation of methylene bischalcones has been discovered during deprotection of methoxymethyl (MOM) groups from trihydroxychalcones. Studies on this methylenation reaction were carried out leading to a mechanism hypothesis and extended to other chalcones and to dihydrochalcone, acetophenone, benzophenone and flavone derivatives. This new method was applied to the rapid synthesis of a natural product, piperanduncin C. These original methylene bis compounds were also evaluated for their antiparasitic activity.
DOI : 10.1002/ejoc.201400104
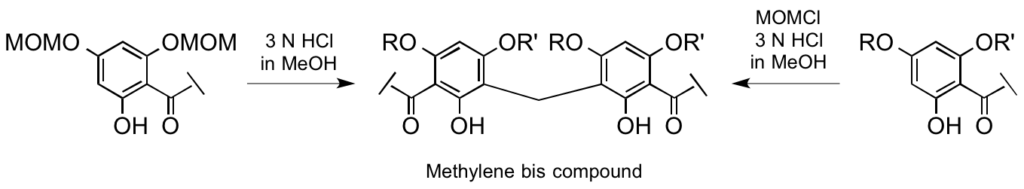
M. Thévenin, S. Thoret, P. Grellier and J. Dubois ; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4885-4892.
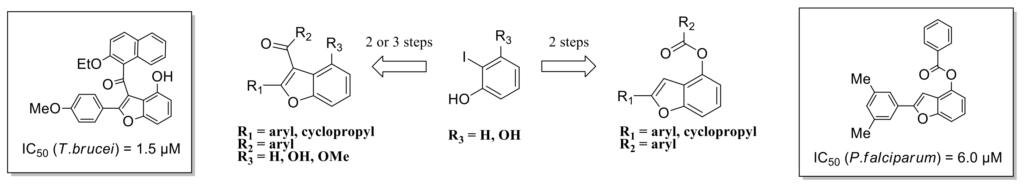
Synthesis of polysubstituted benzofuran derivatives as novel inhibitors of parasitic growth.
A series of polysubstituted benzofuran derivatives was easily and rapidly prepared using a tandem Sonogashira coupling/cyclization reaction. Subsequent acylation afforded a small library of 39 new compounds that were assayed in cellulo on Plasmodium falciparum and Trypanosoma brucei parasites. Some of them exhibited good inhibitory activity on T. brucei proliferation.
DOI : 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.07.002
Fluorescent probe design
In our search for new antiparasitic compounds, we observed that activity improvement on isolated FTase was not seen on parasite. To determine if this discrepancy was due to ineffective entry of the molecule into parasites new fluorescent probes were designed to detect small molecules inside protozoan parasites.
This project was supported by Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (DCM20121225779) including a PhD thesis grant.
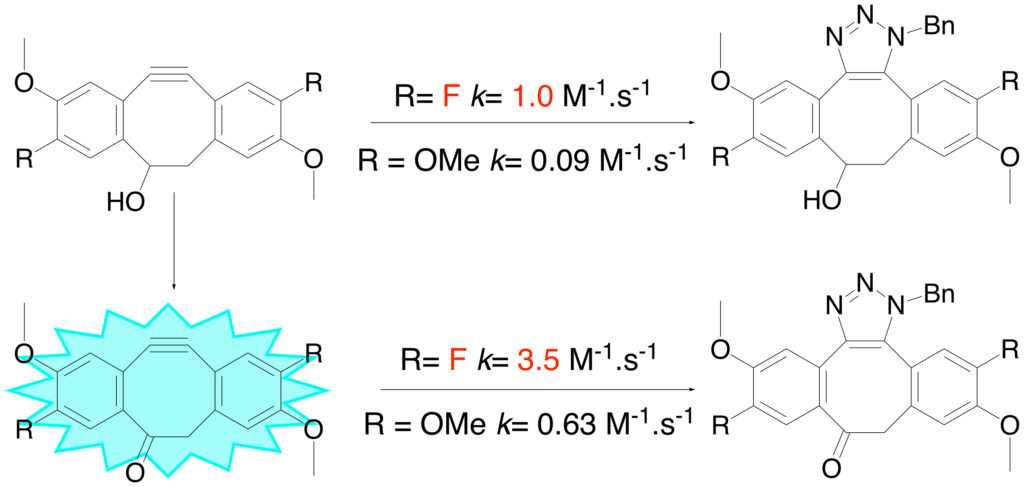
Terzic, V. ; Pousse, G. ; Méallet-Renault, R. ; Grellier, P. ; Dubois; J. J. Org. Chem. 2019, asap
Dibenzocyclooctynes: effect of aryl substitution on their reactivity toward Strain-Promoted Akyne-Azide Cycloaddition.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b00895.
V. Terzic, PhD thesis, Paris-Saclay University, 2016
Utilization of “click” chemistry for the vizualisation of drug entry into portozoan parasites
http://www.theses.fr/2016SACLS190

